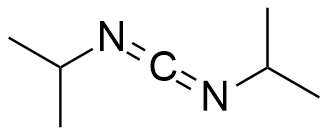
DIC has the advantage over N,N’-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide in solid phase peptide syntheses that the urea by-product is more soluble in organic solvents and hence more readily separated from the polymer support.
CAS: 693-13-0
Synonym: N,N’-Diisopropylcarbodiimide
Properties
Purity
≥99.0%
Molecular Formula
C7H14N2
Molecular Weight
126.20 [gr/mol]
Appearance
Colorless to very faintly brownish-yellow liquid
Storage Conditions
Store in cool place.
Store under inert gas. Moisture sensitive.
Applications
- Used in combination with OxymaPure® in peptide synthesis.
Studies
- OxymaPure/DIC: An Efficient Reagent for the Synthesis of a Novel Series of 4-[2-(2-Acetylaminophenyl)-2-oxo-acetylamino] Benzoyl Amino Acid Ester Derivatives A. El-Faham, Z. A. Marhoon, A. Abdel-Megeed, and F. Albericio Molecules, 2013, 18, 14747-14759.
- Solid-phase peptide synthesis: from standard procedures to the synthesis of difficult sequences I. Coin, M. Beyermann, and M. Bienert Nature Protocols, 2017, 2, 3247-3256.
Read Article - Thermal Stability Assessment of Peptide Coupling Reagents Commonly Used in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Jeffrey B. Sperry*, Christopher J. Minteer, JingYa Tao, Rebecca Johnson, Remzi Duzguner, Michael Hawksworth, Samantha Oke, Paul F. Richardson, Richard Barnhart, David R. Bill, Robert A. Giusto, and John D. Weaver III
Org. Process Res. Dev. 2018, 22, 9, 1262–1275